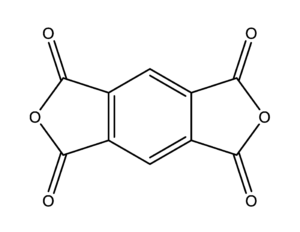
CAS Number: 89-32-7
Synonyms:
- 1,2,4,5-Benzenetetracarboxylic dianhydride
- 1,2,4,5-Benzenetetracarboxylic 1,2,4,5-dianhydride
- Pyromellitic acid dianhydride
PMDA is a solid, with a melting point of 284-288°C. It has been around since the 1950s and was initially used as a curing agent for epoxy resins. It is both highly rigid and reactive upon melting. Cured resins have a high glass transition temperature and exhibit brittleness. As a result, the use of PMDA with epoxies has been replaced by other dianhydrides such as BTDA for select applications.
Debuting in the 1960s, PMDA has now become a workhorse dianhydride to produce polyimide films and varnishes for electrical insulation. PMDA is also used in thermoplastic resin recycling processes as an additive to rebuild molecular weight.
PMDA is used in large volumes, typically 10k metric tons per year and is the nearest to a commoditized status of any dianhydride. Several manufacturers offer this molecule, with production focused in China. PMDA’s availability and pricing are subject to significant fluctuations based on the supply of durene in the global market.
RELEVANT ARTICLES
Entry 5 – Magnet Wire and Polyimide Varnish/Enamel as Primary Insulation for Electrical Wire
Welcome to the fifth entry of The Dianhydrides Diaries, [...]
What Are Epoxy Composites?
Epoxy composites are a type of polymer material that uses [...]
Entry 4 – High Glass-Transition Temperatures from Dianhydride-cured Epoxy
Welcome to the fourth entry of The Dianhydrides Diaries, [...]



